Access Methods
is a program or a hardware mechanism that moves data between the computer and an outlying device such as a hard disk (or other form of storage) or a display terminal.
Types of Access Methods
- Ethernet
- CSMA/CD
Short for Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection, a set of rules determining how network devices respond when two devices attempt to use a data channel simultaneously (called a collision). Standard Ethernet networks use CSMA/CD to physically monitor the traffic on the line at participating stations. If no transmission is taking place at the time, the particular station can transmit. If two stations attempt to transmit simultaneously, this causes a collision, which is detected by all participating stations.
- Switched Ethernet
An Ethernet LAN that uses switches to connect individual hosts or segments. In the case of individual hosts, the switch replaces the repeater and effectively gives the device full 10 Mbps bandwidth (or 100 Mbps for Fast Ethernet) to the rest of the network. This type of network is sometimes called a desktop switched Ethernet. In the case of segments, the hub is replaced with a switching hub.
Traditional Ethernets, in which all hosts compete for the same bandwidth, are called shared Ethernets. Switched Ethernets are becoming very popular because they are an effective and convenient way to extend the bandwidth of existing Ethernets.
- Ethernet Frame
- PoE (Power over Ethernet)
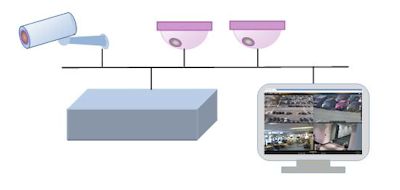
Power over Ethernet (POE) is a technology that lets network cables carry electrical power.
For example, a digital security camera normally requires two connections to be made when it is installed:
A network connection, in order to be able to communicate with video recording and display equipment
A power connection, to deliver the electrical power the camera needs to operate
Power over Ethernet brings many advantages to an installation:
- Time and cost savings - by reducing the time and expense of having electrical power cabling installed. Network cables do not require a qualified electrician to fit them, and can be located anywhere.
- Flexibility - without being tethered to an electrical outlet, devices such as IP cameras and wireless access points can be located wherever they are needed most, and repositioned easily if required.
- Safety - POE delivery is intelligent, and designed to protect network equipment from overload, under-powering, or incorrect installation.
- Reliability - POE power comes from a central and universally compatible source, rather than a collection of distributed wall adapters. It can be backed-up by an uninterruptible power supply, or controlled to easily disable or reset devices.
- Scalability - having power available on the network means that installation and distribution of network connections is simple and effective.
- Token Ring
A Token Ring network is a local area network (LAN) in which all computers are connected in a ring or star topology and a bit- or token-passing scheme is used in order to prevent the collision of data between two computers that want to send messages at the same time.
This is how its work:
- Empty information frames are continuously circulated on the ring.
- When a computer has a message to send, it inserts a token in an empty frame (this may consist of simply changing a 0 to a 1 in the token bit part of the frame) and inserts a message and a destination identifier in the frame.
- The frame is then examined by each successive workstation. If the workstation sees that it is the destination for the message, it copies the message from the frame and changes the token back to 0.
- When the frame gets back to the originator, it sees that the token has been changed to 0 and that the message has been copied and received. It removes the message from the frame.
- The frame continues to circulate as an "empty" frame, ready to be taken by a workstation when it has a message to send.

- FDDI
Abbreviation of Fiber Distributed Data Interface, a set of ANSI protocols for sending digital data over fiber optic cable. FDDI networks are token-passing networks, and support data rates of up to 100 Mbps (100 million bits) per second. FDDI networks are typically used as backbones for wide-area networks.
An extension to FDDI, called FDDI-2, supports the transmission of voice and video information as well as data.
Abbreviation of Fiber Distributed Data Interface, a set of ANSI protocols for sending digital data over fiber optic cable. FDDI networks are token-passing networks, and support data rates of up to 100 Mbps (100 million bits) per second. FDDI networks are typically used as backbones for wide-area networks.
An extension to FDDI, called FDDI-2, supports the transmission of voice and video information as well as data.
- ATM
Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) is a switching technique used by telecommunication networks that uses asynchronous time-division multiplexing to encode data into small, fixed-sized cells. This is different from Ethernet or Internet, which use variable packet sizes for data or frames. ATM is the core protocol used over the synchronous optical network (SONET) backbone of the integrated digital services network (ISDN).
Ref:


No comments:
Post a Comment